Embark on a journey through the realm of Key Economic Indicators for Investment Decisions, where data reigns supreme and guides strategic financial choices with precision and foresight.
Explore the pivotal role of economic indicators in shaping investment decisions and unlocking profitable opportunities in the dynamic market landscape.
Introduction to Economic Indicators
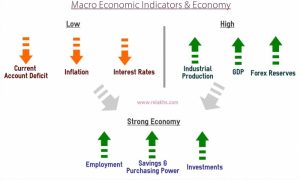
Economic indicators are essential tools used by investors to assess the health and direction of an economy. These indicators provide valuable insights into various aspects of economic performance, helping investors make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies.
Types of Economic Indicators
- Leading Indicators: Leading indicators are signals that change before the economy starts to follow a particular pattern. Examples include stock prices, building permits, and consumer confidence surveys.
- Lagging Indicators: Lagging indicators are signals that change after the economy has already started to follow a particular pattern. Examples include unemployment rates and corporate profits.
- Co-incident Indicators: Co-incident indicators are signals that change at the same time as the economy. Examples include industrial production and retail sales.
Commonly Used Economic Indicators in Investment Analysis
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders. It is a key indicator of economic performance.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking employment. It reflects the overall health of the job market.
- Inflation Rate: The inflation rate measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise. It is crucial for assessing the purchasing power of consumers and the overall cost of living.
- Consumer Confidence Index: The consumer confidence index measures the level of optimism or pessimism consumers have about the economy’s future. It can impact consumer spending and investment decisions.
Key Economic Indicators for Investment Decisions

The field of investment decisions relies heavily on various economic indicators that provide insights into the overall health and stability of an economy. Understanding key indicators such as GDP, inflation rates, interest rates, and unemployment rates is crucial for making informed investment choices.
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) as a Key Indicator
GDP is a fundamental economic indicator that measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders. For investors, GDP growth signifies a healthy economy with increasing business activity, consumer spending, and overall prosperity. A rising GDP often translates to higher corporate profits and potential investment opportunities.
Inflation Rates Impact on Investment Decisions
Inflation rates reflect the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising within an economy. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of money over time, affecting the returns on investments. Investors typically seek to protect their portfolios from inflation by choosing assets that can outpace inflation or by adjusting their investment strategies accordingly.
Significance of Interest Rates in Investment Strategies
Interest rates set by central banks influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment decisions. Changes in interest rates can impact the profitability of investments, particularly in fixed-income securities like bonds. Investors often adjust their asset allocation based on interest rate forecasts to optimize returns and manage risks effectively.
Unemployment Rates Influence on Investment Choices
Unemployment rates indicate the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking employment but unable to find jobs. High unemployment rates can lead to reduced consumer spending, lower business revenues, and overall economic uncertainty. Investors monitor unemployment trends to assess the stability of the labor market and potential impacts on industries and sectors in their investment portfolios.
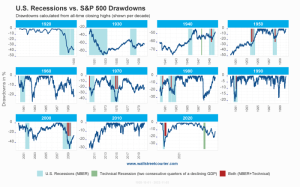
Stock Market Indicators

Stock market indicators such as the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average play a crucial role in guiding investment decisions for investors.
Relevance of Stock Market Indices
Stock market indices like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average are widely followed benchmarks that provide investors with a snapshot of the overall market performance. These indices track the performance of a specific group of stocks and are used by investors to gauge the health of the economy, assess market trends, and make informed investment decisions.
Impact of Market Volatility
Market volatility refers to the rapid and unpredictable changes in stock prices. High volatility can make investment decisions more challenging as it introduces uncertainty and risk. Investors may become more cautious during periods of high volatility, leading to increased market downturns or corrections. It is important for investors to understand how market volatility can affect their investment portfolios and adjust their strategies accordingly to mitigate risks.
Stock Market Performance Indicators and Investor Sentiment
Stock market performance indicators, such as price-to-earnings ratio, dividend yield, and earnings per share, can influence investor sentiment. Positive performance indicators can boost investor confidence and lead to increased investment activity, driving stock prices higher. On the other hand, negative performance indicators can create uncertainty and lead to a decrease in investor sentiment, resulting in market declines. It is essential for investors to monitor these indicators to make informed decisions and stay ahead of market trends.
Foreign Exchange Indicators
Foreign exchange indicators play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions. Understanding how currency exchange rates, trade balances, currency reserves, and geopolitical events impact foreign exchange markets is essential for investors.
Role of Currency Exchange Rates in Investment Choices
Currency exchange rates directly influence the returns on international investments. Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to significant gains or losses for investors. For example, a strengthening of the investor’s home currency against the foreign currency can reduce returns on investments denominated in that foreign currency.
Impact of Trade Balances and Currency Reserves on Investment Decisions
Trade balances and currency reserves of a country can affect its currency’s value. A country with a trade surplus tends to have a stronger currency, while a trade deficit may weaken its currency. Investors consider these factors when making decisions on foreign investments.
Significance of Geopolitical Events on Foreign Exchange Markets and Investments
Geopolitical events such as elections, conflicts, and policy changes can create volatility in foreign exchange markets. Investors closely monitor these events as they can impact currency values and investment returns. For instance, political instability in a country can lead to a depreciation of its currency.
As we conclude our exploration of Key Economic Indicators for Investment Decisions, it becomes evident that leveraging these crucial data points can lead to informed and successful investment strategies that stand the test of time.
Question & Answer Hub
How do economic indicators impact investment decisions?
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of an economy, influencing investment strategies based on factors like growth potential and stability.
Why is GDP considered a key economic indicator for investments?
GDP serves as a vital metric to gauge economic performance, helping investors assess the overall health and trajectory of a country’s economy.
What role do stock market indices play in investment decisions?
Stock market indices like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average offer benchmarks to track market trends, aiding investors in making informed choices.
How do geopolitical events impact foreign exchange indicators?
Geopolitical events can create volatility in foreign exchange markets, influencing currency exchange rates and investment decisions.