
As GDP as an Economic Indicator takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, serves as a key measure of economic performance, offering insights into a country’s financial health and overall well-being. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of GDP as an economic indicator.
GDP as an Economic Indicator
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a key economic indicator that measures the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. It provides a comprehensive snapshot of a nation’s economic activity and performance.
Calculation of GDP
GDP can be calculated using three main approaches:
- The production approach: Summing up the value added at each stage of production.
- The income approach: Totaling up all incomes earned by individuals and businesses in the economy.
- The expenditure approach: Adding up all expenditures on final goods and services in the economy.
Use of GDP as a Measure of Economic Performance
GDP is widely used to assess the economic health and performance of a country. Some common applications of GDP include:
- Comparing the economic growth rates of different countries over time.
- Assessing the standard of living and economic well-being of a nation’s residents.
- Formulating and evaluating economic policies to stimulate growth or address economic downturns.
Importance of GDP
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a crucial economic indicator that provides a comprehensive snapshot of a country’s economic performance. It measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year.
Significance of GDP
GDP serves as a key indicator of economic health and growth, reflecting the overall size and strength of an economy. It helps policymakers, investors, and businesses make informed decisions by providing insights into the trends and performance of different sectors within the economy.
- GDP can indicate whether an economy is expanding or contracting, helping to identify periods of recession or growth.
- It allows for international comparisons of economic performance and standard of living among countries.
- GDP influences government policies, such as fiscal and monetary measures, to stimulate economic activity or control inflation.
Comparing GDP with Other Economic Indicators
While GDP is a vital economic indicator, it is not the only measure of economic health. Other indicators, such as unemployment rates, inflation, consumer spending, and trade balances, provide additional insights into different aspects of the economy. These indicators complement GDP by offering a more nuanced view of economic conditions and trends.
It is essential to consider a range of economic indicators in conjunction with GDP to gain a comprehensive understanding of an economy’s overall performance.
Limitations of Using GDP as the Sole Measure
Despite its importance, GDP has limitations as a measure of economic well-being. It does not account for factors such as income distribution, quality of life, environmental sustainability, or informal economic activities. As a result, relying solely on GDP to assess economic health may overlook important aspects of societal welfare and development.
- GDP does not reflect disparities in income distribution and may mask inequalities within a population.
- It does not consider the environmental impact of economic growth, such as pollution or resource depletion.
- Informal economic activities, such as household work or unreported transactions, are not captured in GDP calculations.
Components of GDP

The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is composed of several key components that help measure the economic performance of a country. These components include consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Consumption
Consumption refers to the total amount spent by households on goods and services. It is the largest component of GDP and reflects the overall demand in the economy. When consumers are confident and have disposable income, they tend to spend more, leading to an increase in GDP. Conversely, if consumers are saving more and spending less, it can slow down economic growth.
Investment
Investment includes business spending on capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and structures. It also encompasses residential construction. Investments contribute to the expansion of businesses and the creation of jobs, ultimately stimulating economic growth. When businesses are investing in new projects and expanding their operations, GDP tends to rise. On the other hand, a decrease in investment can lead to a decline in GDP.
Government Spending
Government spending refers to expenditures on goods and services by federal, state, and local governments. This component includes spending on infrastructure, defense, education, and healthcare. Government spending can directly impact GDP by creating demand for goods and services, as well as providing public services that support economic activity. An increase in government spending can boost GDP, while a decrease can have the opposite effect.
Net Exports
Net exports represent the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A positive net export value indicates that a country is exporting more than it is importing, contributing positively to GDP. On the other hand, a negative net export value implies that a country is importing more than it is exporting, which can have a negative impact on GDP. Changes in global trade patterns, exchange rates, and domestic production can influence a country’s net exports and, consequently, its GDP growth.
Relationship between GDP and Economic Health
When it comes to understanding a country’s economic health, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) plays a crucial role. GDP is considered a key indicator of the overall economic performance of a nation, reflecting the total value of all goods and services produced within its borders. As such, fluctuations in GDP can have significant implications for the country’s economic well-being.
Impact of GDP on Economic Health
- GDP growth is often associated with increased economic activity, such as higher employment rates and rising incomes. This can lead to improved living standards and overall prosperity within a country.
- Conversely, a decline in GDP growth or a recession can result in job losses, reduced consumer spending, and overall economic hardship for the population.
- Stable and consistent GDP growth is essential for long-term economic stability, as it indicates a healthy and growing economy.
Fluctuations in GDP and Economic Trends
- Changes in GDP can serve as indicators of broader economic trends, such as periods of expansion, recession, or stagnation within a country.
- A rising GDP may indicate a booming economy with increased production and consumption, while a falling GDP could signal economic challenges or a slowdown in activity.
- By analyzing GDP trends over time, policymakers, businesses, and investors can make informed decisions about economic conditions and potential future developments.
Real-World Examples of GDP Impact
- During the 2008 financial crisis, many countries experienced sharp declines in GDP as a result of the economic downturn. This led to widespread job losses, reduced consumer confidence, and significant challenges for businesses.
- In contrast, countries that have consistently high GDP growth rates, such as China and India in recent years, have seen rapid economic development, increased investments, and improvements in infrastructure and living standards.
- The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused a global economic shock, with many countries facing GDP contractions due to lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and reduced consumer demand.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are statistics or data points that provide insights into the overall health of an economy. These indicators help measure economic performance, track changes in the economy, and forecast future trends.
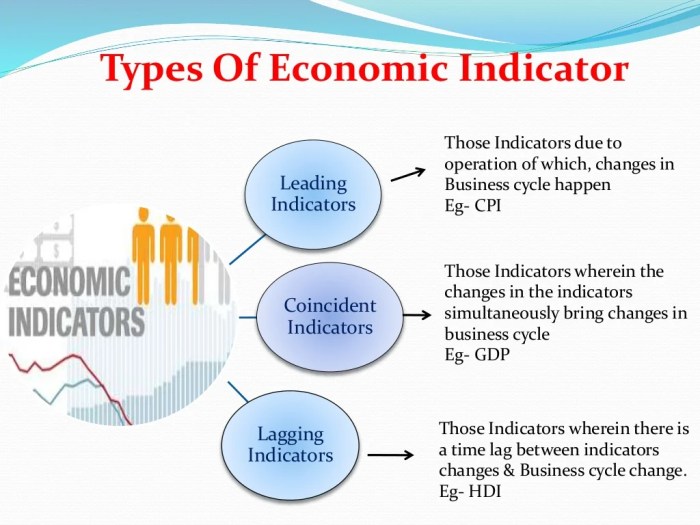
Types of Economic Indicators
There are three main types of economic indicators: leading, lagging, and coincident indicators. Each type plays a unique role in assessing the current state of the economy and predicting its future direction.
- Leading Indicators: Leading indicators change before the economy as a whole changes. They are used to predict future trends and can provide early warnings of potential economic turning points. Examples include building permits, consumer confidence, and stock market performance.
- Lagging Indicators: Lagging indicators, on the other hand, change after the economy has already begun to follow a particular trend. These indicators confirm long-term trends and are often used to confirm a pattern that has already been identified. Examples include unemployment rate and inflation rate.
- Co-incident Indicators: Co-incident indicators change at the same time as the overall economy, providing real-time information about the current state of the economy. These indicators reflect the current economic conditions and include measures such as industrial production and retail sales.
Role of Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are crucial tools used by policymakers, businesses, and investors to make informed decisions. Policymakers rely on these indicators to formulate economic policies, while businesses use them to assess market conditions and plan their strategies accordingly. Investors use economic indicators to gauge the performance of financial markets and make investment decisions.
In conclusion, GDP stands tall as a vital economic indicator, shedding light on a nation’s economic prowess and growth trajectory. By understanding its components and implications, one can navigate the complex landscape of global economics with clarity and foresight.
Popular Questions
What is GDP and why is it important?
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, is a crucial measure of a country’s economic performance as it reflects the total value of all goods and services produced within its borders.
How is GDP calculated?
GDP is calculated by adding up consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Why is GDP not the sole measure of economic health?
GDP does not account for factors like income distribution, quality of life, or environmental sustainability, making it an incomplete measure of overall economic well-being.







