Kicking off with Economic Indicators for Recession Prediction, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, providing an intriguing overview of how economic indicators play a crucial role in predicting recessions.
Exploring the different types of economic indicators and their significance in analyzing the economy, this discussion delves into the world of leading, lagging, and coincident indicators.
ECONOMIC INDICATORS
Economic indicators are statistical data that provide insights into the overall health and performance of an economy. These indicators help analysts and policymakers understand the current economic conditions, predict future trends, and make informed decisions.
Types of Economic Indicators
- Leading Indicators: Leading indicators are signals that change before the economy starts to follow a particular trend. They are used to predict future economic activity. Examples include stock market performance, building permits, and consumer confidence surveys.
- Lagging Indicators: Lagging indicators tend to change after the economy as a whole does. They confirm long-term trends and are used to confirm the direction of the economy. Examples include unemployment rate, corporate profits, and labor costs.
- Co-incident Indicators: Co-incident indicators change along with the economy. They provide real-time information about the current state of the economy. Examples include industrial production, retail sales, and GDP growth rate.
Analyzing the Economy with Economic Indicators
Economic indicators play a crucial role in analyzing the economy by providing valuable information about various aspects such as employment, inflation, production, consumer spending, and business investment. Analysts use a combination of leading, lagging, and coincident indicators to assess the current economic situation, identify trends, and predict future economic growth or potential downturns. By monitoring these indicators, policymakers can make informed decisions to stabilize the economy, promote growth, and prevent recessions.
LEADING INDICATORS
Leading economic indicators are variables that tend to change before the economy as a whole changes. They are used to predict the future direction of the economy and provide insights into potential economic downturns.Specific leading indicators commonly used for predicting recessions include:
Stock market performance
A decline in stock prices can indicate investor pessimism and a potential economic slowdown.
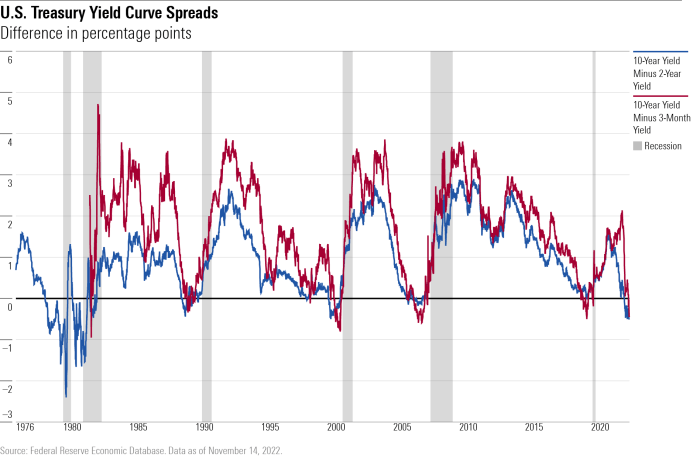
Yield curve inversion
When long-term interest rates fall below short-term rates, it can signal a recession is on the horizon.
Consumer confidence
A drop in consumer confidence can lead to reduced spending, impacting overall economic activity.
Housing market indicators
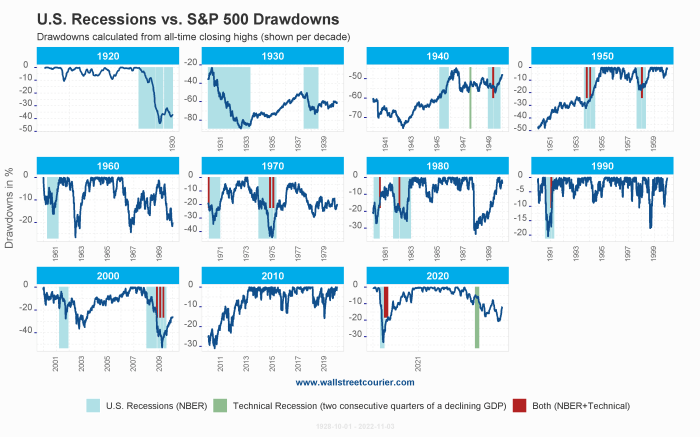
Decreases in housing sales or construction can foreshadow an economic downturn.The relationship between leading indicators and economic downturns is based on the idea that certain changes in these indicators can precede a recession. For example, a decrease in consumer spending or business investments can be reflected in leading indicators before the broader economy shows signs of contraction.Changes in leading indicators can signal a potential recession by providing early warning signs of economic weakness.
By monitoring these indicators closely, policymakers, businesses, and investors can better prepare for possible downturns and take proactive measures to mitigate the impact.
LAGGING INDICATORS
Lagging economic indicators are metrics that confirm trends and patterns that have already occurred in the economy. Unlike leading indicators that provide insight into future economic changes, lagging indicators reflect historical data and are used to confirm the current state of the economy.Examples of lagging indicators relevant to recession prediction include:
Unemployment rate
High unemployment rates are typically seen during or after a recession, indicating a slowdown in economic activity.
Consumer spending
A decrease in consumer spending can be a lagging indicator of a recession, as people tend to cut back on non-essential purchases during economic downturns.
Corporate profits
Declining corporate profits can signal a weakening economy and potentially confirm a recession.The significance of lagging indicators in confirming a recession lies in their ability to validate the trends indicated by leading indicators. While leading indicators may signal a potential recession, lagging indicators provide concrete evidence of economic changes that have already taken place.Lagging indicators help assess the impact of economic changes by offering a retrospective view of the economy.
By analyzing lagging indicators, policymakers, businesses, and investors can understand the full scope of economic shifts and make informed decisions based on historical data.
Impact of Lagging Indicators
Lagging indicators play a crucial role in painting a comprehensive picture of the economy. They offer valuable insights into the aftermath of economic shifts and provide a solid foundation for understanding the long-term effects of recessions. By analyzing lagging indicators alongside leading indicators, economists can gain a more holistic view of the economic landscape and make more accurate predictions about future trends.
COINCIDENT INDICATORS

Coincident economic indicators are statistics that provide real-time information about the current state of the economy. Unlike leading indicators that predict future economic trends, coincident indicators move in conjunction with the business cycle, reflecting the current economic conditions.
Examples of Coincident Indicators
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders. A rising GDP indicates economic growth, while a declining GDP may signal a recession.
- Industrial Production: This indicator tracks the output of industrial sectors like manufacturing, mining, and utilities. An increase in industrial production suggests economic expansion, while a decrease could indicate a downturn.
- Employment Levels: The number of employed individuals in an economy can provide insights into the strength of the labor market and overall economic activity. Rising employment is typically associated with economic growth.
Coincident indicators play a crucial role in recession prediction by offering a real-time snapshot of the economy’s current health. Since they move in sync with the business cycle, changes in coincident indicators can confirm or validate forecasts made using leading indicators.
How Coincident Indicators Reflect the Current State of the Economy
- Coincident indicators provide immediate information on the economic performance of a country, offering insights into factors like production, employment, and overall economic activity.
- By analyzing coincident indicators, economists and policymakers can gauge the strength of the economy in real-time and make informed decisions about monetary and fiscal policies.
- Fluctuations in coincident indicators can help identify shifts in the business cycle, such as the onset of a recession or the beginning of an economic recovery.
How Coincident Indicators Help Validate Recession Predictions
- When leading indicators point towards a potential recession, monitoring coincident indicators can confirm whether the economy is indeed entering a downturn.
- If coincident indicators like GDP, industrial production, and employment levels show a simultaneous decline, it strengthens the case for a recession prediction based on leading indicators.
- By comparing data from coincident indicators with historical trends, economists can validate recession forecasts and adjust policy responses to mitigate the impact of an economic downturn.
In conclusion, understanding economic indicators for recession prediction is vital for assessing the health of the economy and anticipating potential downturns. By examining leading, lagging, and coincident indicators, analysts can gain valuable insights into the future economic landscape.
Helpful Answers
What are leading economic indicators?
Leading economic indicators are metrics that change before the economy starts to follow a particular pattern or trend. They are used to predict changes in the economic landscape.
How do lagging indicators confirm a recession?
Lagging indicators, such as unemployment rates, confirm a recession by reflecting changes that have already occurred in the economy. They provide a retrospective view of economic performance.