
Economic Indicators for Global Trade sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. From defining economic indicators to exploring their impact on global trade, this topic delves deep into the intricacies of the global economy.
Economic Indicators for Global Trade
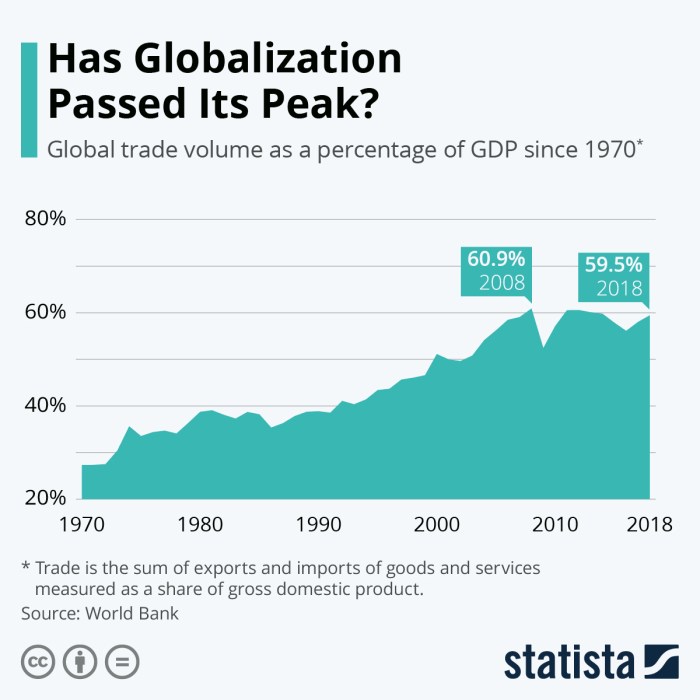
Economic indicators are statistical data that provide insights into the economic performance of a country or region. When it comes to global trade, these indicators play a crucial role in assessing the overall health and performance of the global economy.
Significance of Economic Indicators in Assessing Global Trade
Economic indicators help in understanding the health and performance of the global economy by offering valuable information on key aspects such as inflation, unemployment rates, GDP growth, consumer spending, and trade balances. By analyzing these indicators, policymakers, investors, and analysts can gauge the strength of the economy and anticipate potential risks or opportunities.
Examples of Key Economic Indicators for Global Trade
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP represents the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders. It is a vital indicator of economic performance and growth.
- Trade Balance: This indicator measures the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A positive trade balance indicates that a country exports more than it imports, while a negative balance suggests the opposite.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): CPI measures the changes in the prices of a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households. It helps in assessing inflation levels and the purchasing power of consumers.
- Industrial Production Index: This indicator tracks the output of industrial sectors such as manufacturing, mining, and utilities. It provides insights into the overall economic activity and production capacity.
Role of Economic Indicators in Predicting Trends in Global Trade
Economic indicators play a crucial role in predicting trends and forecasting changes in global trade dynamics. By analyzing trends in key indicators such as GDP growth, trade balances, and consumer spending, experts can anticipate shifts in demand, supply, and trade patterns. This predictive capability helps businesses, policymakers, and investors make informed decisions and adapt to changing market conditions in the global trade landscape.
Types of Economic Indicators
When it comes to analyzing global trade, different types of economic indicators play a crucial role in providing insights into the overall economic health of countries and regions. These indicators can be broadly categorized into leading, lagging, and coincident indicators, each offering unique perspectives on the state of the economy.
Leading Economic Indicators
Leading economic indicators are data points that change before the economy starts to follow a particular trend. These indicators are used to predict future economic trends and are closely watched by policymakers, investors, and businesses to anticipate potential changes in the economy. In the context of global trade, leading indicators can provide early signals of shifts in demand, production levels, and overall economic activity in different countries.
- Example: New orders for capital goods, stock market performance, building permits
Lagging Economic Indicators
Lagging economic indicators are data points that change after the economy has already started to follow a particular trend. These indicators confirm trends that have already occurred and are used to assess the overall health of the economy. In the context of global trade, lagging indicators can provide insights into the impact of previous economic events on trade activity.
- Example: Unemployment rate, inflation rate, labor costs
Co-incident Economic Indicators
Co-incident economic indicators are data points that change at the same time as the economy is following a particular trend. These indicators provide a real-time snapshot of the current economic conditions and are often used to validate the accuracy of leading indicators. In the context of global trade, co-incident indicators can offer a timely assessment of the current state of trade flows and economic activity.
- Example: Industrial production, retail sales, GDP growth rate
Importance of Analyzing a Combination of Economic Indicators
While each type of economic indicator offers valuable insights into the economy, analyzing a combination of leading, lagging, and coincident indicators provides a more comprehensive view of global trade trends. By considering multiple indicators, decision-makers can better understand the complex interplay of factors influencing trade activity and make more informed decisions regarding investments, trade policies, and business strategies.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Global Trade
Changes in economic indicators play a crucial role in shaping global trade policies and agreements. These indicators provide valuable insights into the overall economic health of countries, influencing decisions related to trade regulations, tariffs, and international partnerships.
Influence of Economic Indicators on Global Trade Activities
- GDP: The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country is a key economic indicator that directly impacts global trade. A strong GDP growth often leads to increased trade activities as it signals a robust economy with higher consumer spending and demand for goods and services.
- Inflation Rates: Fluctuations in inflation rates can affect global trade by influencing currency values and pricing strategies. High inflation may lead to decreased purchasing power, impacting international trade volumes.
- Employment Data: Employment figures reflect the labor market conditions, which in turn impact consumer confidence and spending patterns. Unemployment rates can influence the demand for imports and exports, thereby affecting global trade flows.
Historical Events Demonstrating the Impact of Economic Indicators on Global Trade
- Great Recession (2008): The global financial crisis in 2008, triggered by factors like subprime mortgage lending and credit default swaps, led to a significant decline in global trade volumes. Economic indicators such as GDP contraction and rising unemployment rates impacted trade relationships worldwide.
- Oil Crisis (1973): The oil embargo imposed by OPEC countries in response to geopolitical tensions led to a spike in oil prices and inflation rates. This event had a profound impact on global trade patterns, particularly in industries heavily reliant on oil imports.
Correlation between Economic Indicators and Industry Performance in Global Market
- Manufacturing Sector: Changes in GDP growth rates can directly influence the performance of the manufacturing sector in the global market. A strong GDP often translates to increased demand for manufactured goods, boosting trade activities in this industry.
- Service Sector: Employment data and consumer spending trends play a critical role in shaping the performance of the service sector in global trade. High employment rates and disposable income levels can drive demand for services, impacting trade flows.
Monitoring and Interpreting Economic Indicators

Monitoring and interpreting economic indicators is crucial for analyzing global trade trends and making informed decisions in the business landscape. By understanding these indicators, businesses can adapt their strategies and navigate the ever-changing international market effectively.
Significance of Timing and Frequency
Timing and frequency play a vital role in tracking economic indicators for real-time decision-making in global trade. It is essential to monitor these indicators regularly to capture any sudden shifts or emerging trends that could impact trade activities.
- Regular monitoring allows businesses to stay ahead of market changes and adjust their operations promptly.
- Real-time data provides valuable insights into the current economic conditions, helping businesses make informed decisions quickly.
- Tracking indicators frequently ensures that businesses are aware of both short-term fluctuations and long-term trends in global trade.
Best Practices for Interpreting Economic Indicators
Effectively interpreting economic indicators is key to making informed decisions in the global trade landscape. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Compare multiple indicators to get a comprehensive view of the economy and trade conditions.
- Understand the historical context of the indicators to identify patterns and trends accurately.
- Stay updated on economic news and events that could influence the indicators and global trade.
Challenges and Limitations
Relying solely on economic indicators for predicting global trade trends comes with certain challenges and limitations:
“Economic indicators may not always provide a complete picture of the market dynamics and can be influenced by external factors beyond the scope of traditional indicators.”
- Unexpected events or geopolitical factors can impact global trade independently of economic indicators.
- Interpreting indicators incorrectly can lead to misguided decisions and missed opportunities in the international market.
- Over-reliance on indicators may overlook qualitative aspects of the market that are essential for trade analysis.
In conclusion, Economic Indicators for Global Trade serves as a vital tool for understanding the complexities of the global market landscape. By analyzing key indicators and their influence on trade dynamics, stakeholders can make informed decisions to navigate the ever-evolving world of international commerce.
Common Queries
How do economic indicators impact global trade policies?
Economic indicators can influence the formulation of trade policies by providing insights into the overall health of the economy, which in turn affects decision-making processes.
Why is it important to analyze a combination of economic indicators?
Analyzing a combination of indicators offers a more holistic view of global trade trends, enabling stakeholders to make well-rounded assessments and predictions.
Can economic indicators accurately predict global trade trends?
While indicators provide valuable data, relying solely on them for predictions may have limitations due to the complex and dynamic nature of global trade.





